The Vital Link: Spine Health, Good Posture, and Treatment Options
The human spine is a marvel of engineering. This flexible column of bones, discs, and muscles provides structure, support, and mobility for our entire body. It houses and protects the spinal cord, a vital pathway for nerve signals that control everything from movement to sensation.
However, neglecting good posture can put a strain on this complex system. Poor posture can lead to pain, stiffness, and even long-term spinal problems. This article delves into the connection between spine health and good posture, explores the consequences of slouching, and offers a comprehensive guide on achieving and maintaining proper alignment. We’ll also shed light on various treatment options for addressing existing spinal issues.
Understanding Your Spine
The spine is made up of 24 individual bones called vertebrae. These bones are connected by strong ligaments and cushioned by intervertebral discs. The discs act as shock absorbers, distributing pressure evenly throughout the spine.
Here’s a breakdown of the key components of the spine:
- Vertebrae: Each vertebra has a bony body and a hollow canal in the center that houses the spinal cord. There are different types of vertebrae with varying shapes and functions depending on their location in the spine.
- Intervertebral Discs: These discs are gel-filled cushions located between each vertebra. They absorb shock, provide flexibility, and allow for movement in the spine.
- Spinal Cord: This bundle of nerves runs through the canal in the center of the vertebrae. It carries messages between the brain and the rest of the body, controlling movement, sensation, and other bodily functions.
- Spinal Nerves: These nerves branch out from the spinal cord and travel through openings between the vertebrae. They connect the spinal cord to muscles, skin, and other organs throughout the body.
The Importance of Good Posture
Good posture is the alignment of your body in a way that minimizes stress on the spine and joints. It allows your muscles to work efficiently and supports your body weight evenly. Here are some key benefits of good posture:
- Reduced Back Pain: Proper alignment reduces strain on the muscles and ligaments that support the spine, leading to less pain and stiffness.
- Improved Flexibility: Good posture allows for a wider range of motion in your joints, promoting flexibility and agility.
- Enhanced Breathing: When your spine is aligned, your chest can expand more fully, allowing for deeper and easier breathing.
- Boosted Confidence: Good posture can make you appear taller and more confident.
- Reduced Risk of Injury: Proper alignment distributes forces evenly, minimizing the risk of injuries like muscle strains and spinal disc problems.
Consequences of Poor Posture
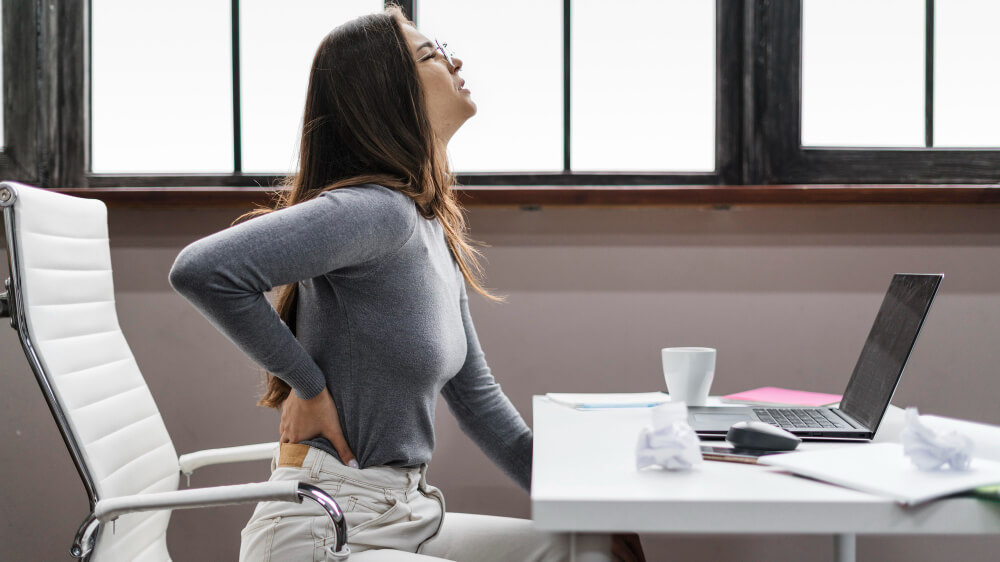

Slouching or maintaining poor posture for extended periods can have detrimental effects on your spine and overall well-being. Here are some potential consequences:
- Back Pain: One of the most common issues associated with poor posture is back pain. Slouching puts extra strain on the muscles and ligaments that support the spine, leading to pain and stiffness.
- Neck Pain: Poor posture can also lead to neck pain and headaches. When you hunch forward, the muscles in your neck and upper back become strained.
- Rounded Shoulders: Slouching can lead to rounded shoulders, which can affect your posture and make it difficult to stand tall.
- Spinal Deformities: In severe cases, long-term poor posture can contribute to spinal deformities like kyphosis (hunchback) or scoliosis (curvature of the spine).
- Digestive Issues: Poor posture can put pressure on the internal organs, potentially leading to digestive problems like heartburn and constipation.
- Decreased Energy Levels: Poor posture can restrict breathing and make you feel tired and sluggish.
Achieving and Maintaining Good Posture
The good news is that good posture can be learned and maintained with practice. Here are some practical tips to improve your posture:
- Stand Tall: Imagine a string pulling you up from the crown of your head. Keep your shoulders back and relaxed, with your ears in line with your shoulders.
- Engage Your Core: Tighten your abdominal muscles to support your lower back. Don’t suck in your stomach, but gently pull your belly button towards your spine.
- Bend at the Knees: When picking something up, bend at your knees and hips, keeping your back straight. Avoid bending over with a rounded back.
- Maintain a Neutral Neck Position: Your head should be balanced on top of your spine, not jutting forward or tilted down.
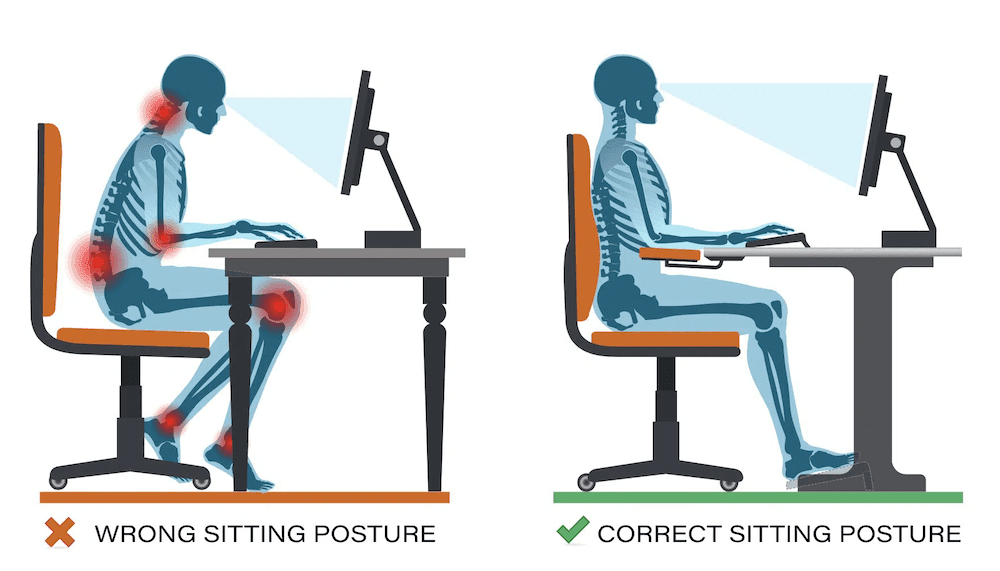
- Ergonomic Workspace: Ensure your workstation is ergonomically designed. Your chair should provide good back support, your feet should be flat on the floor, and your computer screen should be at eye level.
